Glossary of Logistics Terms
At Logisto, we have 15+ years of working in the industry and yet still, we are so often caught out by just how many terms and acronyms and abbreviations are used in the world of logistics. If you find yourself Googling 3 letter acronyms to understand FOB, BSA or TMS, then you are not alone. We are doing the same as there is always some new acronym that comes along! To make life easier we have taken our knowledge and coupled that with scouring the internet, journals and books to compile a mega glossary of logistics terms.
In this section of the Knowledge Centre, we have grouped the terms of the logistics into different categories to align with their area of reference in order to help make it easier to find what you are looking for. Of course, if you are interested, then please read them all, but if not (and we suspect not!), we recommend going to the relevant section to locate the term you need.
If you have an acronym or a term that isn’t covered in the list below, then please contact us and we will help you find the answer and add it to our glossary.
Thank you
LOGISTO Team
General Logistics Terms
Anti-competitive activity
Anti-competitive behaviour is an important part of Logistics, just like other areas of business. Specifically for logistics, it includes dumping (when a country or company sells products at a loss to drive away competitors), price fixing (when companies agree to set higher prices together to prevent competition from lowering prices), and government subsidies (that allow a company or industry to operate at a loss, preventing competitors from entering the market).
Application Program Interface – API
APIs are critical to automating the data flow and information exchange. This is transforming the logistics industry. One example is that an API automatically updates the inventory of an ecommerce store every time a product is ordered and leaves the fulfilment centre.
B/L or BOL - Bill of Lading - B/L or BOL
A bill of lading (BL or BoL) is a legal document issued by a carrier to a shipper that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being carried. A bill of lading also serves as a shipment receipt when the carrier delivers the goods at a predetermined destination.
Dimensional Weight - DimWt
Dimensional weight, also known as ‘volumetric weight’, is a pricing technique for commercial freight transport, which uses an estimated weight that is calculated from the length, width and height of a package. The shipping fee is based upon the dimensional weight or the actual weight, whichever is greater.
General Rate Increase - GRI
An amount by which ocean carriers increase their base rates due to increased demand or exceptional market circumstances.
House Air Waybill - HAWB
This is a receipt issued by a freight forwarder for goods. It differs from an AirWay Bill in that the freight forwarder does not own or operate the aircraft.
Hazardous Materials- HazMat
Any item or chemical which, when being transported or moved in commerce, is a risk to public safety or the environment. A hazardous substance is any substance that has one or more inherent hazardous properties. This includes flammability, explosiveness, toxicity, and the ability to oxidise. The CoSHH Regulations cover most substances that are hazardous to health - and these substances can take a variety of different forms.
For more information on HazMat, please see the gov website:
Link: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2002/2677/contents/made
International Commercial Terms - INCO
The Incoterms (or INCO) are a series of commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commerce law. They define the rights and responsibilities of each party to a sales contract and clarify when the legal possession of goods transfers from the buyer to the seller. Please see our detail section on IncoTerms here.
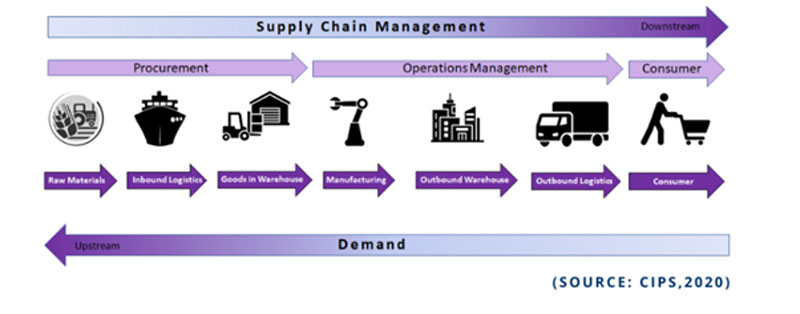
Supply Chain and Supply Chain Management
A supply chain is a focus on the core activities within our organisation required to convert raw materials or component parts through to finished products or services. This is the full life cycle of a products design and development, production, transportation and sale.
Volumetric weight
Volumetric weight, also known as ‘dimensional weight’, is a pricing technique for commercial freight transport, which uses an estimated weight that is calculated from the length, width and height of a package. The shipping fee is based upon the dimensional weight or the actual weight, whichever is greater.
Transportation Terms
Air Waybill - AWB
An airway bill or AWB is a document that accompanies goods shipped by an international courier, which allow for tracking. It serves as a receipt of goods by an airline, as well as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier.
British Maritime Law Association (BMLA)
The Association has two principal functions. Firstly, it acts as an adviser to the UK Government and has responsibility for maritime legislation and regulation. Secondly, it co-operates with the international parent body, the CMI, in research hand assisting in the drafting of international instruments for the harmonisation of maritime law
Comité Maritime International – CMI
The Comité Maritime International is a non-governmental not-for-profit international organization established in Antwerp in 1897, the object of which is to contribute by all appropriate means and activities to the unification of maritime law in all its aspects.
Demurrage
Demurrage is a charge that is applied to containers (or vehicles) that are left at the port, rail yard or delivery location longer than their allotted free time. Shippers will often begin incurring this fee the day after the last free day and it is charged per container / per day until the container is picked up. At a port, this is usually 4-7 days after unloading.
Full-Container Load - FCL
A full shipping container consigned to a single party.
House Bill of Lading – (HBOL)
House Bill of Lading is a formal acknowledgment that the carrier has received the consignment for shipment post-inspection. It is an assurance that the consignment damage-free and is ready to be shipped to the consignee. Any damage incurred during the shipping becomes the liability of the carrier.
IATA - International Air Transport Association
The IATA issues rules and guidance for transporting goods by air internationally.
Intermodal container
An intermodal container, often called a shipping container, is a large standardized shipping container, designed and built for intermodal freight transport, meaning these containers can be used across different modes of transport – from ship to rail to truck – without unloading and reloading their cargo.
Less – than Container Load (LCL)
LCL (Less-than-container Load) is a shipping term used where one shipper alone does not contract a full container load as their volume is not sufficient. The remaining volume of a shipping container is filled by multiple orders or goods.
Less-than Truckload – LTL
Less than truckload freight shipping (LTL) is used for the transportation of small freight or when freight doesn’t require the use of an entire trailer. This can be pallets or boxes.
Master Air Waybill - MAWB
An air waybill (AWB) or air consignment note is a receipt issued by an international airline for goods and an evidence of the contract of carriage. It is not a document of title to the goods. The air waybill is non-negotiable and is issued by a carrier to a freight forwarder upon receiving a shipment to a named location, as agreed in the shipping terms.
NVOCC - Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier
A NVOCC is an ocean carrier that transports goods under its own House Bill of Lading (or equivalent documentation) without operating ocean transportation vessels.
Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit – TEU
A TEU or Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit is an exact unit of measurement used to determine cargo capacity for container ships and terminals.
This measurement is derived from the dimensions of a 20ft standardized shipping container. Because standard containers can be 20 or 40ft in length the capacity of a container ship can depend on the ratio of the two sizes.
In order to avoid confusion and standardize a ship’s capacity, the number of containers a ship can load is translated into a number of 20ft containers and that measurement is known as TEU. For example, one forty-foot container is two TEUs.
Shipping container
A shipping container is a box with the required strength suitable to withstand shipment, storage, and handling.
Transportation Management System - TMS
A transportation management system (TMS) is specialized software for planning, executing and optimizing the shipment of goods. A TMS often connects the ERP with legacy transportation management systems.
3PL & Warehousing Terms
3rd Party Logistics – 3PL
Refers to the outsourcing of logistics services like warehousing, distribution, and fulfilment; increasingly common in the logistics industry as businesses specialize their core functions and turn to 3PL vendors for more efficient product handling.
Activity-based Costing - ABC
A costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each.
Container Freight Station - CFS
A container freight station is a distribution facility where import and export shipments are consolidated and de-consolidated. CFS's are a key component in any supply chain moving interior point intermodal (IPI) freight.
Demand Planning - DP
Demand planning is forecasting demand for a particular service or product so that it can be manufactured and delivered when a customer needs it. It allows lower lead times and a better use of resources.
Enterprise Asset Management - EAM
Enterprise asset management (EAM) is a combination of software, systems and services used to maintain and control operational assets and equipment.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is a type of supply chain management that moves goods from customers back to the sellers or manufacturers. ... Reverse logistics can also include processes where the end consumer is responsible for the final disposal of the product, including recycling, refurbishing or resale
Uniform Product Code - UPC
The Universal Product Code (UPC; redundantly: UPC code) is a barcode symbology that is widely used worldwide for tracking trade items in stores.
UPC (technically refers to UPC-A) consists of 12 digits that are uniquely assigned to each trade item. Along with the related EAN barcode, the UPC is the barcode mainly used for scanning of trade items at the point of sale, per GS1 specifications.
Warehouse Management System - WMS
Software applications that allow for the automation and optimization of warehouse, distribution, and fulfilment logistics.
A warehouse management system (WMS) consists of software and processes that allow organizations to control and administer warehouse operations from the time goods or materials enter a warehouse until they are ready for fulfillment.
Commercial Invoice - CI
The final bill for charges due on a shipment of goods. CIs are used to clear Customs by providing the total cost on which duties will be assessed.
Certificate of Origin - COO
A statement that tells where goods were manufactured; C/Os are used when applying for duty-free entry on imports from countries which US has trade agreements with.
Cost, Insurance, and Freight - CIF
CIF means that a seller is providing the goods, their transportation, and insurance for the cost paid by the buyer. Other costs, including import and local delivery, are the responsibility of the buyer. Those who imports goods from China are often familiar with this term. New importers should use caution, as foreign manufacturers may give the impression that CIF includes all costs.
COGS - Cost of Goods Sold
The direct costs of manufacturing a product, not to be confused with overhead, marketing, or logistics costs.
GATT - General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
An attempt by many countries around the world to create a legal framework to eliminate barriers to trade and commerce by reducing tariffs. GATT was started in 1948 and led to the creation of the World Trade Organization in 1995.
An electronic document that must be filed before a vessel or aircraft departs. It lists
VAT - Value-Added Tax
A type of tax used within the UK and Europe. Taxes are assessed on sales of most goods and services within a country and on some imports. VAT is paid by the seller to the government. Some people favour VAT as a way to make taxation reflect spending. Others object to VAT as a system that taxes the lowest-earning buyers proportionately higher than wealthier buyers.
WTO - World Trade Organization
In 1995, the WTO replaced GATT as the intergovernmental organization that handles trade between nations. It oversees and implements international economic agreements and governs the rules of trade.